When a Nerve Fiber Is Polarized the Concentration of
In an unmyelinated fiber in a human the conduction rate is about 2 msec. When a nerve fiber is polarized the concentration of A.
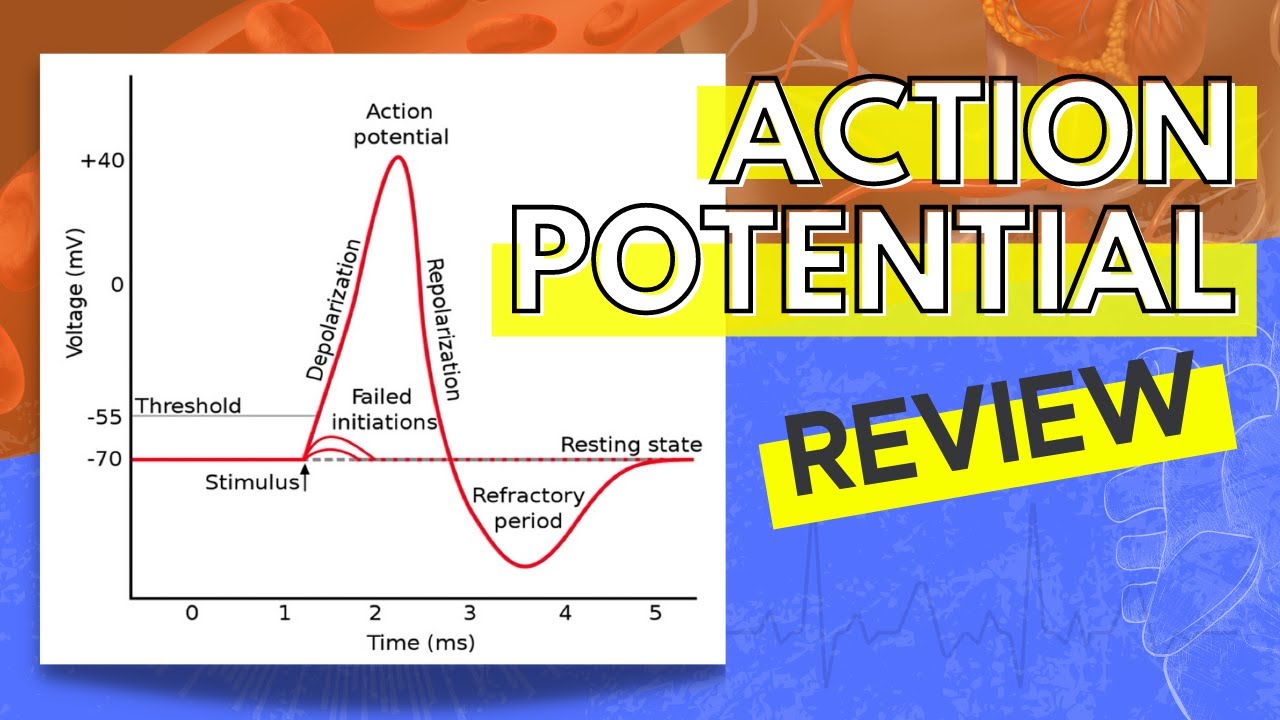
7 2 Resting Graded And Action Potential Medicine Libretexts
For instance the nerve impulse of a mammal is one twenty meters per second whereas nerve impulse of a Frog is 30 meters per second.

. Mechanisms of generation of nerve impulse and its conduction along an axon. Sodium ions is higher on the outside of its membrane and potassium ions are higher on the. An amount of K and Na is always get out across the membrane with the help of leakage channels but NaK pump which is present on the membrane helping in to restore the ions to the suitable side.
Sodium ions is higher on the inside of its membrane and potassium ions are higher on the outsideC. It begins when the neuron receives a chemical signal from another cell or some other type of stimulus. When a stimulus is applied at a site on the polarised membrane the membrane at that site becomes freely permeable to Na.
Na and K are higher on the outside of the membrane. Na and K is higher on the inside of the membrane. When an electrical stimulus is received by a nerve fibre an action potential is generated.
The transmission of nerve impulse would rely upon the diameter of the fibre. Myelinogenesis is the process by which myelination of the nerve fiber takes place. A nerve impulse is a sudden reversal of the electrical gradient across the plasma membrane of a resting neuron.
Na is higher on the outside of the membrane and K is higher on the inside. Small myelinated fibers may conduct as slowly as 12 msec whereas large motor and sensory fibers conduct at a rate of 50 to 70 msec in humans. This relatively short change in polarization is thought to be caused by the movement of positively charged sodium ions externally to the inner side of the cell consequences in nerve impulse transfer.
Answer a Polarisation of the membrane of a nerve fibre During resting condition the concentration of K ions is more inside the axoplasm while the concentration of Na ions is more outside the axoplasm. When a nerve fiber is polarized the concentrationofA. When the neurotransmitter molecules bind to ligand-gated ion channels on the receiving cell they may cause depolarization of that cell causing it to undergo its own action potential.
Polarization is established by maintain the concentrations of Na is higher on the outside and K is higher on the inside. Na is higher on the inside of the membrane and K is higher on the outside. This results in a positive charge inside and negative charge outside the nerve fibre.
A Polarisation of the membrane of a nerve fibre During resting condition the concentration of K ions is more inside the axoplasm while the concentration of Na ions is more outside the axoplasm. Some neurotransmitters also cause hyperpolarization and a single cell may receive both types of inputs See video. The action potential is the transient depolarization that happens during nerve conduction when inside the neuron fibre gets positively charged.
Within these nodes ions are exchanged across cell membranes during depolarization resulting in an action potential. As a result the potassium ions move faster from inside to outside as compared to sodium ions. As the sodium ions quickly enter the cell the internal charge of the nerve changes from -70 mV to -55 mV.
In the peripheral nervous system the myelinogenesis is contributed by the Schwann cells whereas in the CNS it is being contributed by the oligodendroglial cells. The myelin sheath acts as an electrical insulator that is regularly interrupted by the nodes of Ranvier. When a nerve fiber is polarized the concentration of sodium ions is higher on the outside of its membranes and potassium is higher on the inside every neuron has.
Inside becomes positive relative to the outside. During the depolarization phase the gated sodium ion channels on the neurons membrane suddenly open and allow sodium ions Na present outside the membrane to rush into the cell. It is around twenty times faster compared to that of the non-medullated nerve fibres.
The membrane becomes permeable to sodium ions than to potassium ions. When the nerve cell is sufficiently stimulated sodium channels in the cell membrane open and sodium ions flood into the cell depolarizing the cell membrane the charge reverses. As a result the potassium ions move faster from inside to outside as compared to sodium ions.
The sheath of Schwann cell wraps the axon by about 80-100 times. A nerve fiber becomes polarized when the resting potential of the membrane changes. This is known as the polarization of membrane or polarized nerve.
If the stimulus is strong enough to reach threshold an action potential will take place is a cascade along the axon. Biology questions and answers. Neuronal synapses chemical I hope that helps.
The reversal of charge is called an action potential. When a nerve fiber is polarized the concentrations of Na and K are higher on the inside of the membrane. When a stimulus is applied at a site on the polarised membrane the membrane at the site A becomes freely permeable to Na which leads to a rapid influx of Na followed by the reversal of the polarity at that site and the membrane is depolarised.
This leads to a rapid influx of Na followed by the reversal of the polarity at that site ie the outer surface of the membrane becomes negatively charged and the inner side becomes positively charged. Several factors influence nerve conduction velocity other than whether or not the axon is myelinated. It starts out with an unequal distribution of charges- the.
Na and K is higher on the outside of the membrane. Peripheral nerve fibers are often classified according to their size and degree of myelination. Sodium and potassiumions is higher on the inside of its membraneB.
Distribution And Orientation Of Nerve Fibers And Myelin Assembly In A Brain Section Retrieved By Small Angle Neutron Scattering Scientific Reports

Chapter 9 Part I Review Mrs Chirichella 1 In The Cns Myelin Is Formed By A Schwann Cells B Oligodendrocytes C Astrocytes D Microglial Cells Ppt Download

Muscle Fiber Membrane Potential An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

No comments for "When a Nerve Fiber Is Polarized the Concentration of"
Post a Comment